
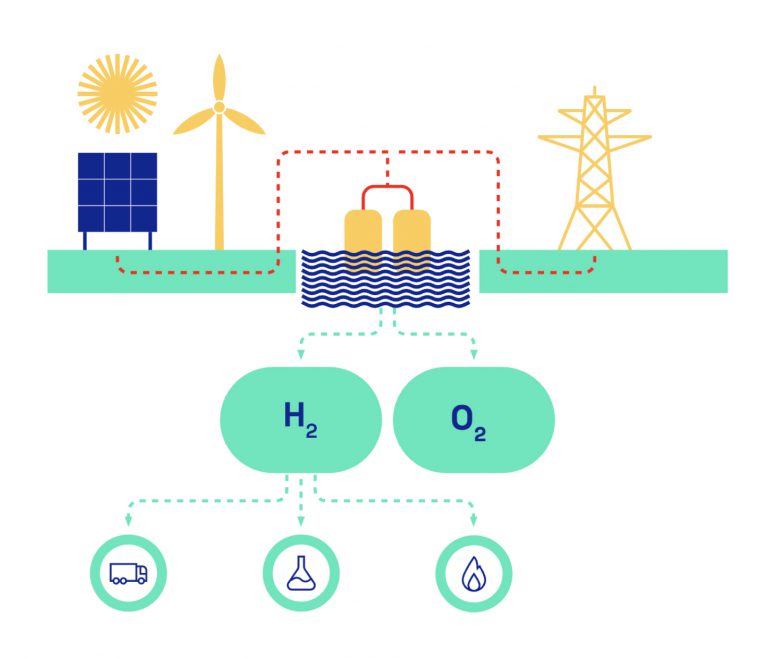
Electrolysis consists of three levels of architecture: the cell, the stack, and the production unit. The electrolyser cell contains two conductive metal electrodes (anode and cathode), connected to a direct current generator, and separated by an electrolyte which can be an aqueous solution or membrane.
When assembled, the cells form stacks, often built in series which, supplemented by auxiliary equipment (electrical controls, water treatment, piping, compressor, etc.) form the electrolysis production units.
We develop, finance, build and operate low-carbon molecule production plants in France and in the iberian peninsula. Discover the application sectors of our products !
